5621. Find a multiple
There are n positive
integers, some of them may be equal. Select f
(1 ≤ f ≤ n) of them in such a way that their sum
is divisible by , that is, there exists an integer such that
n * k =
(sum of the selected numbers)
Input. The first line contains the number of
integers n (n ≤ 10000). Each of the following n lines contains one
integer not greater than 15000.
Output. If no such subset of numbers exists, print 0.
Otherwise, print
the number of selected integers in the first line, followed by the selected
numbers themselves (one per line) in any order. If there are multiple suitable
subsets, print any of them.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
5 1 2 3 4 1 |
2 2 3 |
SOLUTION
sequences, mathematics
Algorithm analysis
Let d1, d2,
…, dn be the input numbers.
Consider all their partial sums:
si = d1
+ … + di
Since there are exactly n partial sums, among all the values of si mod n there must be either two
that are equal or at least one that is zero.
If for some indices a – 1 < b it holds that
sa-1 mod n = sb mod n,
then the sum da + … + db is divisible by n.
Therefore, the sequence of
numbers da, da + 1, …, db is a valid solution.
If there exists an i such that si mod n
= 0, then the
sequence d1, d2, …, di forms a valid solution.
Example
Let’s consider the given
example. Compute all the partial sums:
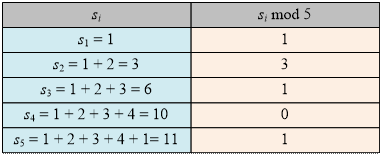
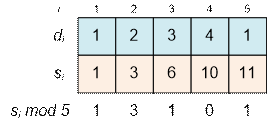
There are several valid
subsets. For example:
·
since s1 = s3, then d2 + d3
= 5 is
divisible by 5.
·
since s1 = s5, then d2 + d3
+ d4 + d5 = 10 is divisible by 5.
·
since s3 = s5, then d4 + d5
= 5 is
divisible by 5.
·
since s4 = 0, then d1 + d2
+ d3 + d4 = 10 is divisible by 5.
Algorithm implementation
We’ll store the input
numbers in an array d. The array r will be used to record partial sums: if s = d1
+ … + di, then assign r[s] = i.
#define MAX 10100
int d[MAX], r[MAX];
The desired set of numbers
whose sum is divisible by n, will be da, da+1, …, db. Print their count b – a + 1, followed by the numbers
themselves – one per line.
void print(int
a, int b)
{
printf("%d\n",b
- a + 1);
for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
printf("%d\n",d[i]);
}
The main part of the
program. Initialize
the array r with the value -1 and set r[0] = 0 to handle the case
when the sum of the first i numbers is divisible by n.
memset(r,-1,sizeof(r)); r[0] = 0;
Read the number of elements n.
scanf("%d",&n);
Compute the partial sums modulo n in the variable sum.
sum = 0;
for (i = 1; i <=
n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",
&d[i]);
sum = (sum + d[i]) % n;
If a partial sum sum occurs again, print the
desired set of numbers:
dr[sum] + 1, dr[sum] + 2, …, di
if (r[sum] !=
-1)
{
print(r[sum] + 1, i);
break;
}
r[sum] stores
the first index i where the partial sum d1 + … + di produced the remainder sum when divided by n.
else r[sum] =
i;
}